The origin of the beauty of Lanzarote lies in its geology, its natural landscapes, its evolution, and its original materials that make up its geological heritage. Volcanoes, cliffs, caves, beaches, lava flows, jameos, calderas and islets, have turned the island into a geologically unique place in the Atlantic.
Definition
A Geosite, or Site of Geological Interest, is an “area that is part of the geological heritage of a natural region as constantly shows one or several characteristics that are considered significant in its geological history” (García Cortés and Carcavilla, 2013).
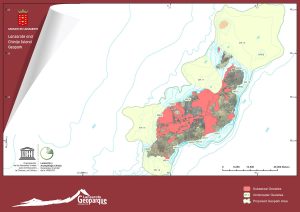
In our Geopark, there are 49 geosites on land and 19 underwater. 68 places can be marked on the map.
Next, there is a description of land sites according to the Specific Collaboration Agreement Report CIL-IGME to carry out scientific-technical research of the use of the volcanic resources of Lanzarote (createad by Inés Galindo, Nieves Sánchez, Carmen Romero and Juana Vegas), in 2014.
LZ04 Salinas del Río
These are the oldest in the Canary Islands as they were exploited in the 16th Century. They are on a [...]
LZ05 Peñas de Tao
The best example in Lanzarote of the presence of numerous erratic blocks, reaching more than 30 m in height. The [...]
LZ06 Tubo volcánico de La Corona- Atlántida
It formed after the eruption of Volcán de La Corona around 25 ka BP. It is more than 7.6 km [...]
LZ07 Valles colgados de Famara
It includes some complex valleys when it comes to their evolution and morphology, and lacks heads and mouths. The are [...]
LZ08 Valle de Temisa
It corresponds to a broad basin with a soft longitudinal bed and a broad transversal profile typical of “U” valleys. [...]
LZ09 El Jable
A wind sand corridor of active organic wind sand that runs through the island north to south, from Caleta de [...]
LZ10 El Cuchillo-Mosta-Montaña Cavera
This is the area with the highest concentration of surtseyan cones in all the Canary Islands. The three volcanic buildings [...]
LZ11 La Santa
La Santa is a geosite formed by coastal marine deposits (sandstone and carbonated gravel, grindstone type) containing abundant fossils such [...]
LZ12 Las Laderas
Paleo-cliff corresponding to the topographic end of Risco de Famara. It is totally disconnected from the current coastline. At its [...]
LZ13 Barranco de Tenegüime
This is a clear example of a valley with a transversal “V” profile. A straight ravine where the erosion of [...]